Achieving your organizational goals requires defined processes to guide your team in daily operations. However, coordinating all tasks to ensure fast, accurate completion and accountability can be challenging, primarily in sizable teams.
That’s where workflows come into play.
We know what you’re thinking: aren’t workflows and processes the same? Not exactly. They’re similar but serve distinct purposes.
Buckle up for the ultimate workflow vs. process showdown to understand their role in your business and see how they maximize efficiency.
Defining Workflows and Processes
A workflow is a sequence of tasks to complete a particular process. It includes the steps or actions your team must execute to streamline operations and make processes efficient.
This interconnected, granular flow of tasks and actions can be:
- Sequential – including dependent activities (you can’t execute one without completing the previous)
- Parallel – allowing simultaneous completion of independent actions (e.g., preparing multiple customer orders)
A business process is a series of steps for achieving an organizational goal. They include all the details for completing specific tasks, specifying who should execute them and when. They often have decision points, allowing responsible parties to choose an action according to a situation or helping them understand when to route activities or escalate problems.
You have three types of business processes:
- Operational – essential actions for increasing revenue by delivering value to customers (e.g., customer service, marketing, sales, etc.)
- Support – activities facilitating core business processes (e.g., recruitment, bookkeeping, payroll, etc.)
- Management – systems for planning, executing, monitoring, controlling, and evaluating all processes (e.g., logistics, compliance, risk, and performance management)
Key Differences Between Workflows and Processes
Workflows streamline business operation tasks by detailing the standardized steps to take in a particular order to achieve a specific goal (complete a process). They help you see the big picture of that goal.
Processes provide the structural framework for workflows by detailing all activities to reach a general goal, giving the big picture of long-term objectives.
Processes guide your team, answering the What, Who, and When.
Workflows focus on the How. They help your team understand how to complete the task flow in that framework.
As such, processes are strategic, while workflows are tactical. Also, the former exists without the latter, while workflows are process-dependent.
Focus and Goals: Workflows and Processes

Workflows have a micro-level, task-oriented focus, acting as visual roadmaps to guide detailed execution. They emphasize automation and help optimize operations by providing the fastest path to completing sequential steps.
Key aspects of workflows:
- Focus on micro-level tasks
- Serve as visual roadmaps
- Include detailed, step-by-step execution
- Centered around automation
- Streamline processes by reducing time spent on individual tasks
The primary goal is to ensure processes are as efficient as possible.
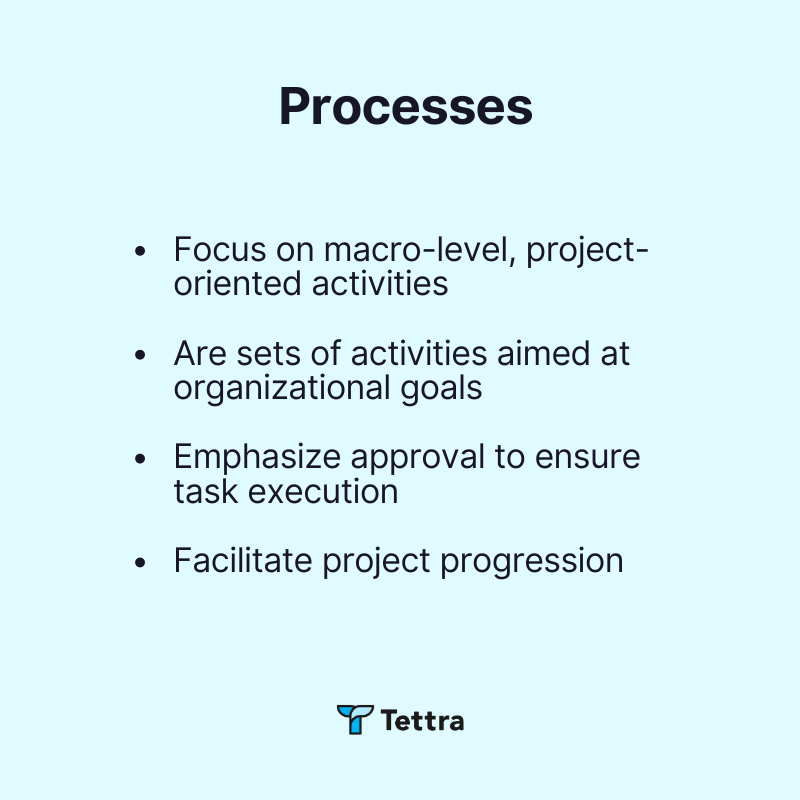
Processes have a macro-level, project-oriented focus, designed as sets of activities to achieve organizational goals. They emphasize approval and ensure tasks are executed smoothly to advance projects to completion.
Key aspects of processes:
- Focus on macro-level, project-oriented activities
- Structured as sets of activities aimed at organizational goals
- Emphasize approval to ensure task execution
- Facilitate seamless project progression
The primary goal is to ensure projects are completed efficiently and effectively.
The Importance of Workflows & Processes in Organizations
Workflows help teams complete processes quickly, making them more efficient and productive. They know who must do what at every dependent stage of a specific process to execute tasks accurately. That means higher accountability and less micromanagement.
A well-defined workflow helps organize and coordinate operations, streamlining work and reducing errors and delays. It gives a top-level view of business processes, helping automate repetitive tasks and identify and eliminate redundancies.
Processes standardize operations in a company. They keep everyone on the same page, ensuring they accurately complete tasks necessary for accomplishing strategic organizational goals. Think of them as checklists.
Teams wouldn’t know where to start without well-defined business processes. There would be no guarantee of completing repetitive tasks the same way. That would cause errors, negatively impacting efficiency, productivity, and customer satisfaction. A process ensures consistency.
Elements of a Workflow
A workflow has the following crucial elements:
- A series of tasks – individual activities to perform sequentially and logically to avoid bottlenecks like errors and delays
- Actors – individuals responsible for completing the assigned tasks
- Inputs – resources, information from a knowledge base, and documents for executing actions
- Outputs – deliverables, reports, and notifications about completed tasks
Workflows vary across organizations, but all have these essential elements.
Stages of a Workflow
A workflow has three primary stages:
- Planning – defining the goals and objectives, identifying tasks and resources, and visualizing the workflow with flowcharts or diagrams to understand all interactions between steps
- Execution – assigning the planned tasks, determining decision points and dependencies, sharing resources, coordinating with stakeholders, and tracking real-time progress and performance to identify and resolve bottlenecks
- Review – performing final checks and authorizations for approval, finalizing tasks, documenting the process, and generating reports
Breaking down workflows into these phases helps boost efficiency, eliminate data silos, and improve decision-making.
Roles and Responsibilities in Workflows
Workflows don’t function without clearly defined roles and responsibilities (dependent on the process). They help responsible parties understand the expectations, providing insight into the actions to complete to advance the workflow.
All workflow tasks have assignees with specific roles and responsibilities, helping them know what to do within a particular time window. That ensures accountability, seamless coordination and collaboration, and fast, accurate completion.
Real-World Examples of Workflows
The most notable workflow examples include:
- Purchase order approval
- Product return authorization
- Purchase request approval
- Software bug fixing
- Employee recruitment
- Customer or employee onboarding
- Customer service ticket resolution
- Document approval
- Guest reservation
Here’s how a workflow for order processing (part of the order fulfillment process) might look:
- A customer orders products from your website.
- Your workflow management software creates a task and notifies the processing team (or a specific individual).
- They verify the order information, check if the products are available, approve the order, and route it to the fulfillment team.
- The fulfillment team packs the products, labels the package, and notifies the shipping carrier.
- The shipping carrier delivers the package to the customer.
Automating this workflow streamlines the process.
Real-World Examples of Processes
Here are some examples of business processes:
- Loan origination
- Credit approval
- Patient care
- Supply chain management
- Order fulfillment
- Product development
- Customer relationship management
- Employee hiring
- Marketing or sales management
Here’s what an order fulfillment process might include:
- Receive and store inventory.
- Process orders.
- Pick products from a fulfillment center or warehouse.
- Pack the products.
- Ship the package.
- Invoice the customer.
- Deliver the product.
You can create workflows for all these stages to ensure accurate, fast process completion.
Benefits of Effective Workflow Management
Effective workflow management helps teams complete tasks without errors, delays, and other problems, ensuring consistency.
That improves transparency, accountability, efficiency, flexibility, and employee satisfaction. It also reduces costs because fast project completion eliminates the need to hire more staff.
Benefits of Effective Process Management
Effective business process management (BPM) eliminates guesswork, keeping everyone on the same page with clearly outlined processes. It standardizes all operations, helping identify opportunities for improvement.
BPM can improve scalability and agility, streamline customer engagement and retention, boost productivity, and ensure policy compliance. It reduces risks, enables cost-effectiveness, increases efficiency, and helps achieve company goals.
Tools for Workflow and Process Management
Managing workflows and processes requires specialized tools, such as:
- Flowchart software like Lucidchart or Miro
- Workflow management software like Slack or Asana
- BPM software like Nintex or AgilePoint
- Project management software like Wrike or Trello
- Internal knowledge base software like Tettra
Some of these solutions suit multiple purposes. For instance, Slack and Asana offer workflow and project management, while Nintex can also automate workflows.
Tettra also doubles as workflow management software, helping you document business processes and streamline workflows.
It offers a Q&A workflow for capturing questions, a knowledge base for documenting answers, and management features for content updates.
Your team can get instant answers from AI using company documents, store and manage workflows and process maps, and link process maps from tools like Lucidchart, Miro, Figma, and Mural.
The best part? Tettra integrates with productivity tools like Slack, Google Drive, Zapier, and many other products. It’s the ultimate internal knowledge base with workflows to boost productivity.
Software Solutions for Workflow Automation
You can automate workflows with many software solutions, including:
- Kissflow
- Jira
- Bitbucket
- HubSpot
- Jotform
- Cflow
- Nintex
- Zapier
Zapier is perfect for automating workflows across multiple web apps and services.
Techniques for Process Mapping
Process mapping involves creating a visual representation of business processes to define what it takes to complete a project. Process maps illustrate the sequence of steps to complete in a specific order, helping stakeholders understand when each activity and action occurs.
Process maps can also include the parties responsible for the activities and decision dependencies between points in a sequence.
The most prevalent techniques for process mapping include:
- Flowcharts – simplified maps illustrating the sequential steps, inputs, and outputs using mapping symbols
- Process flow diagrams (PFD) – flowcharts visualizing the connections between critical components
- SIPOC diagrams – high-level overviews (value-chain or top-down maps) showcasing the supplier, inputs, process, outputs, and customers
- Detailed process maps – the most comprehensive maps outlining all details across steps and sub-processes, including inputs, outputs, decision points, and contingencies
- Value-stream maps (VPS) – flowcharts visualizing the flow of materials and information necessary to deliver a product or service to customers
- Swim-lane maps – cross-functional diagrams delineating roles across channels and showcasing the connections between steps
Whichever technique you use, you can improve process visibility, comprehension, coordination, collaboration, communication, and decision-making, identify inefficiencies, and plan for contingencies.
Best Practices for Implementing Workflows
Once you break down a process into tasks and define roles and responsibilities, follow these practices to implement workflows:
- Create workflow documentation: Outline the steps, dependencies, decision points, roles, responsibilities, and resources and centralize the information in a knowledge base.
- Use workflow management software: Empower your team with automated repetitive tasks, visual representations of workflows, collaboration features, and insightful reports.
- Use communication tools: Keep everyone on the same page with a central hub for discussions, progress updates, and resource sharing.
- Monitor the performance: Define KPIs (Key Performance Indicators), like the task completion time and error rate, to evaluate each workflow and identify inefficiencies or redundancies.
- Gather employee feedback: Encourages stakeholders to leave notes and comments and make suggestions for higher efficiency.
- Optimize workflows: Regularly review your workflows for continuous improvement (e.g., revise steps, integrate new tools, reallocate resources, etc.) and update relevant documentation to reflect the latest changes.
These practices bring order to workflows and help streamline them for efficiency and productivity.
Best Practices for Implementing Processes
Implementing new processes helps optimize their existing counterparts and workflows and achieve organizational goals faster. Here are the best practices to follow:
- Define goals and objectives: Determine the aims of new processes, ensuring they improve the current processes.
- Create an implementation plan: Outline the timelines, KPIs, potential risks (including a contingency plan), and resource allocation.
- Document your processes: Store them in a knowledge base for seamless access and sharing.
- Design process maps: Help teams understand all tasks in a process through diagrams and flowcharts.
- Coordinate processes: Use BPM tools to assign tasks and delegate responsibilities.
- Provide training: Help your team adapt to new processes and obtain the necessary skills.
- Evaluate and optimize processes: Continuously monitor the progress, ask for feedback, and adjust when necessary.
Careful planning prevents process implementation from disrupting business operations, ensuring continuous improvement.
Challenges in Workflow and Process Management
Managing workflows and processes can be challenging. Here are some roadblocks you may encounter:
- Resistance to change: Employees can be reluctant to adapt to new workflows or processes, often refusing to use new tools or follow a novel chain of command.
- Inconsistent processes: Some stakeholders may take shortcuts to complete tasks faster and make changes without keeping others in the loop, making workflows chaotic.
- Unclear workflows and processes: Not defining and documenting them and clarifying instructions, expectations, and dependencies can prevent stakeholders from understanding their responsibilities.
- Redundant processes: Inefficiencies from unnecessary activities that drain resources and time are massive barriers to workflow and process management.
- Poor communication: Information silos and no real-time collaboration can cause errors, delays, and misunderstandings.
- Tech limitations: Inadequate tools or legacy systems with out-of-date architecture can prevent an organization from quickly adapting to changes.
Let’s see how to overcome workflow and process challenges.
Strategies to Overcome Workflow Challenges
Here’s how to remove obstacles to efficient workflow management:
- Communicate workflow benefits (like reducing errors and frustration and saving time) to prevent resistance to change.
- Document workflows with clear guidelines to avoid misunderstandings.
- Use communication tools for real-time team collaboration and sharing.
- Foster a feedback culture for constant improvement.
- Use intuitive workflow management tools to automate tasks, ensure accountability, get insightful reports, and streamline workflows instead of complicating them.
As you can see, everything boils down to communication, automation, and detailed documentation.
Strategies to Overcome Process Challenges
Here’s how to eliminate roadblocks to efficient process management:
- Get stakeholder buy-in before implementing new processes.
- Document processes to standardize operations and ensure consistency.
- Embrace process mapping to visualize steps for better understanding.
- Use BPM tools with integration capabilities to streamline processes and adapt to changes.
- Regularly review processes to maintain goal alignment and identify and eliminate redundancies.
These strategies can turn your processes into efficiency boosters.
The Role of Automation in Workflows and Processes
Automating workflows and processes is crucial for productivity and efficiency. It puts repetitive tasks on autopilot, saving time and effort and increasing output. Teams can focus on activities that provide value instead of spending precious minutes or weekly hours on routine actions.
Automation also eliminates human error, which can sometimes be costly. When technology does the manual work, complex processes become frictionless and error-free. They become consistent, helping organizations achieve goals without disruptions.
Future Trends in Workflows and Processes
Innovative technologies keep reshaping workflow and process management. Here’s a glimpse into future trends:
- AI-powered workflow optimization: Besides automation, organizations will rely on AI to fill out forms, route approvals, escalate issues, optimize individual workflows, and complete other tasks, significantly saving time and effort.
- AI and ML fusion for predictive analytics: AI-powered tools with machine learning algorithms will become go-to solutions for predicting outcomes and inefficiencies, eliminating redundancies, and forecasting trends, facilitating decision-making.
- BPM and RPA integration: Robotic process automation within BPM tools (without external integrations) will become a run-of-the-mill solution for standardizing and streamlining processes.
- Generative AI: Organizations will use text prompts to accelerate business process discovery, create and automate processes and workflows, get optimization recommendations, and generate reports.
These ground-breaking technologies will revolutionize workflows and processes, driving long-term innovation and success.
Use Tettra To Maximize Your Workflows and Processes
Use Tettra To Maximize Your Workflows and Processes
Workflows and processes are the backbone of efficient business operations. Processes provide structure and standardize how tasks should be done, while workflows ensure that day-to-day tasks are tracked and completed on time.
To truly maximize efficiency, it’s essential to document both workflows and processes. This fosters:
- Seamless collaboration across teams
- Consistency in how tasks are executed
- Easy onboarding for new team members
- Reduced errors and misunderstandings
Tettra elevates this by offering a powerful knowledge base where you can document everything in one place. With Tettra’s AI-powered features, you can:
- Automate the organization of processes and workflows
- Keep documentation up-to-date without manual effort
- Provide quick answers to your team through AI-generated suggestions
Plus, Tettra integrates with tools like Slack, enabling:
- Faster access to critical information
- Streamlined communication without leaving your current workflow
- Immediate resolution of questions right where your team works
Try Tettra for free to unlock AI-powered knowledge management that enhances documentation, collaboration, and process efficiency.