Knowledge gaps are a direct hit to performance and productivity. Think about it: what good is knowledge if it isn’t in the hands of those who need it most?
When teams lack crucial info, tasks stall, and businesses suffer. The ripple effect? Gaps in knowledge emerge, organizations stop to assess, and reactionary analysis halts productivity.
This is why understanding how to identify knowledge gaps, conduct a skills gap analysis, and implement strategies to close knowledge gaps is crucial to your organization.
⭐️ Get your free slide deck and calculate your cost savings.
What Causes Knowledge Gaps at Work?
Knowledge gaps, if left unchecked, can disrupt workflows and hamper productivity. But to tackle them effectively, one must first understand their origins:
- Rapid Technological Advancements: As new technologies emerge, the need for teams to adapt and learn grows. If they lag behind, knowledge gaps manifest.
- Employee Turnover: An experienced employee possesses invaluable organizational knowledge. Their exit, without knowledge transfer, creates a significant knowledge void. Hence, documentation and knowledge-sharing practices are vital.
- Ineffective Knowledge Transfer: Knowledge transfer is more than sharing files or brief explanations. It requires robust processes and a culture of knowledge sharing. In its absence, transitions or role changes can create knowledge discrepancies.
- Absence of Continuous Learning: Consistent training and development are crucial. Without them, employees might not stay updated with industry trends, causing knowledge gaps.
- Organizational Changes: Events like mergers or strategic shifts can disorient the existing knowledge framework. Until a new equilibrium is reached, knowledge disruptions might occur.
To proactively tackle these challenges, knowledge mapping is invaluable. It offers a visual representation of an organization’s collective knowledge, highlighting weak areas that need focus.
When assessing the landscape, ask:
- What crucial information are we missing?
- Are there any bottlenecks in the way knowledge flows within our teams?
- Which processes or systems might be hindering knowledge sharing?
By recognizing these factors and asking the right questions, organizations can adopt a proactive approach, quickly addressing knowledge gaps and even preventing them. This foresight can make the distinction between efficient workflows and operational setbacks.
Identifying Knowledge Gaps
The journey of bridging knowledge gaps begins by acknowledging this void and choosing a process to identify them.
Assessing Current Skills and Knowledge Levels
Awareness is the first step. By assessing the current skills and knowledge levels, organizations gain a clear picture of their strengths and potential areas of improvement.
Techniques to gauge skill levels:
- Surveys: Utilized for collecting feedback on perceived skills and identifying training necessities, surveys help highlight areas employees feel under-equipped in.
- Assessments: These structured tools offer an objective lens to measure skill levels, producing tangible data against preset benchmarks.
- Interviews with Employees: Direct interactions provide depth. They uncover details that might be overlooked in broader instruments, enabling employees to voice their perspectives and training aspirations.
- Feedback from Performance Reviews: These comprehensive evaluations offer insights on an employee’s strengths, developmental areas, and training requisites.
Once you have this information, assessing your knowledge management process is essential.
Here’s how:
- Discovery: Identify all existing knowledge sources to understand what you have and what might be absent.
- Capture: Knowledge comes in diverse forms.
- Explicit Knowledge: Located in documents and records, it’s tangible and accessible.
- Implicit Knowledge: Tied to organizational procedures and ethos, often found in guidelines or protocols.
- Tacit Knowledge: Driven by experience, it’s invaluable but poses documentation challenges.
- Index: Organize the collated information for easy access. Picture creating a library where each information byte has its designated spot.
- Assess: Regularly scrutinize the knowledge base for accuracy, comprehensiveness, and currency.
- Distribute: Ensure knowledge is not only stored but also easily disseminated, fostering collaboration and innovation using tools like skills management software.
Identifying Critical Knowledge Assets
The foundation of any organization lies in its knowledge assets, encompassing collective wisdom, expertise, and information pivotal for innovation and growth. To effectively leverage and protect these assets, a systematic approach is indispensable.
Why Cataloging Knowledge Matters
Cataloging knowledge is crucial for an organization’s productivity. This process includes:
- Taking Inventory: Examine the depth and scope of present knowledge. Identify areas that are underrepresented or outdated.
- Continuous Assessments: A singular assessment is insufficient. Given the ever-evolving nature of business, periodic evaluations, leveraging performance data, and communicating with employees are essential to preemptively identify inefficiencies and address knowledge gaps.
- Scrutiny of Topics and Channels: Investigate each content domain. Thinly populated areas may signify a dearth in training materials or broader knowledge deficiencies.
Knowledge in the digital age is often scattered. Centralize it by:
- Exploring Intranet and Shared Drives: Critical data often lies hidden in these commonly used, yet sometimes overlooked, resources.
- Utilizing Dedicated Platforms: Specialized platforms for internal documentation or departmental needs are potential reservoirs of vital knowledge.
- Surveys and Expert Consultation: Active measures like distributing questionnaires can offer insights into employees’ current knowledge and areas they feel less confident about. Engaging with experts provides clarity on specialized or intricate topics.
Flow of Knowledge Analysis
With 87% of executives confronting a skills gap and predictions indicating 50% of all employees will need reskilling by 2025, understanding the flow of knowledge transfer within an organization is critical. It’s essential for innovation and efficiency, directly impacting the organization’s success.
Knowledge is dynamic, consistently changing and moving. Understanding this flow of knowledge transfer within an organization is vital for promoting innovation and efficiency.
Central to this is the knowledge inventory, enabling organizations to determine:
- Knowledge Sharing Dynamics: Are there established platforms or methods for knowledge dissemination? How prevalent is sharing among team members?
- Access Channels: Understanding where and how employees access information can help pinpoint bottlenecks or gaps. This includes digital platforms, informal discussions, formal meetings, and procedural documents.
- Key Players: Identifying primary knowledge contributors and consistent seekers ensures a smoother knowledge transfer, facilitating cohesive team dynamics.
Failure to manage knowledge transfer can lead to missed deadlines, poor work quality, unsatisfied clients, and increased staff turnover.
Promoting a healthy flow of knowledge requires detailed attention to ensure information is accessible and aligns with business goals. This approach is proactive, addressing current knowledge needs and facilitating continuous learning and adaptation, positioning the organization for sustained growth.
Analyzing Employee Performance Gaps
The collective skill set of a workforce fuels an organization’s success. However, variations in performance often indicate employee performance gaps, possibly due to a lack of knowledge or skill.
Addressing these gaps starts with employing data-gathering methodologies. Progressive businesses today accumulate extensive performance data across varied metrics.
Aggregating data from multiple data sources and employing diverse methodologies ensures a comprehensive perspective on employee competencies and areas needing enhancement. This method, termed cross-validation, boosts the trustworthiness and precision of the results.
Consider a sales team, for instance. Evaluating their data on lead generation and conversions can highlight knowledge shortfalls. Those struggling with lead generation may have gaps in their understanding of building an effective sales pipeline. Likewise, if call handlers consistently take longer on calls, it might indicate a deficiency in their communication skills.
Performance data is a valuable tool. When decoded correctly, it reveals knowledge and skills deficiencies. Identifying these gaps allows organizations to refine their training needs, ensuring employees are primed for success in their roles.
Conducting a Skills Gap Analysis
Skills gap analysis plays a vital role in optimizing workforce performance.
With 89% of executives emphasizing skills as a key determinant in job value and 79% of HR professionals prioritizing skills over traditional hiring metrics, it’s evident that a skills gap analysis is essential.
What is Skills Gap Analysis?
Skills gap analysis identifies the variance between current workforce capabilities and the required skills for optimal job performance. This evaluation is crucial for shaping training initiatives and refining recruitment strategies.
Steps to conduct a skills gap analysis:
- Plan: Initiate your analysis by deciding on its focus: is it an individual, team, or company-wide evaluation? Individual assessments contrast an employee’s skills with their role’s demands, while a team/company assessment ascertains if your staff can collectively handle future challenges or if new hires are needed. This clarity aids in designing precise training programs.
- Identify Important Skills: Define the skills that resonate with your company’s mission and goals. Deloitte suggests, “For future success, organizations should shift their focus from knowledge capture to knowledge creation and transfer, and champion a knowledge-sharing culture as vehemently as they champion tools and platforms.”
- Measure Current Skills: Determine where your employees currently stand using tools like surveys, interviews, performance feedback, and skills management software. A role-specific skills checklist can be instrumental. Note: Training needs might arise from inexperience rather than knowledge absence. In such cases, hands-on training might be more beneficial than structured sessions.
- Act on the Data:
- Training: Address identified gaps with targeted training. Options include workshops, online courses, mentorship, or certification programs.
- Hiring: If gaps are too broad to bridge internally, adapt your hiring process to focus on the necessary skills. Integrate skill assessments, structured interviews, and strategic sourcing.
Skills Gap Analysis Template
To enhance organizational growth and productivity, it’s vital to pinpoint where skills are lacking. Using a skills gap analysis template streamlines this process by offering a consistent and thorough method for reviewing employee abilities.
Key Components of the Template:
- Assessing Current Skills:
- Employee Skill Inventory: Catalog individual skills using resumes, job descriptions, and self-assessments.
- Team Skill Inventory: Gain a collective perspective on the competencies of teams or departments, highlighting strong points and areas needing growth.
- Identifying Critical Knowledge Assets:
- Organizational Needs Analysis: Enumerate crucial skills needed for current and future projects, aligning with the company’s goals and vision.
- Industry Trend Analysis: Stay abreast of emerging skills crucial to your industry.
- Analyzing Employee Performance Gaps:
- Performance Data Collection: Draw from performance reviews, peer evaluations, and self-assessments.
- Skill-to-Performance Mapping: Relate specific skills to performance metrics. For example, does a decrease in sales reflect a deficit in negotiation expertise?
- Conducting a Skills Gap Analysis:
- Skills Matrix: Create a grid displaying employee/team names against vital skills. Mark proficiency levels for a snapshot view of skills distribution.
- Action Steps: Based on insights, determine interventions. Do you need training sessions? Should you recruit for particular roles?
Using a skills gap analysis template, the structured format ensures that every facet of the organization’s skills framework is examined. More than just a diagnostic tool, the template serves as a catalyst, urging organizations to proactively address the identified gaps.
Closing the Gap: Strategies for Filling in the Blanks
Recognizing knowledge gaps is only the first step—addressing them effectively ensures organizational growth.
Providing Comprehensive Training Programs
Given the anticipated talent shortages, 73% of executives forecast the need for reskilling.
Ulrik Juul Christenson from Area9 Group puts in bluntly in an article in the Harvard Business Review:
“Unconscious incompetence is a pervasive and escalating problem, especially in fast-paced industries where knowledge and skills need constant updating. Organizations can only address it with more adaptive, individualized corporate learning programs and by promoting a culture of continues improvement,” Christenson says.
What can organizations do?
They are responding with comprehensive training programs, including workshops, e-learning, and specialized courses.
- Diverse Learning Routes: Organizations can choose from a variety of training formats tailored to their needs, including workshops, e-learning sessions, on-the-job training, and specialized courses.
- Professional Certificates: Training often concludes with a certificate, verifying the employee’s new skills and enhancing their professional trajectory.
- Long-term Career Growth: Continuous learning ensures employees remain at the forefront of industry shifts, not just addressing current knowledge gaps but preparing for future needs.
Adopting Automation Solutions
Artificial intelligence and adaptive technology are revolutionizing how individual knowledge gaps are tackled.
- AI & Personalized Learning: AI offers tailored learning experiences, adjusting to the learner’s rate of progress, leading to better training outcomes.
- Knowledge Sharing Tools: Tools like wikis or management software provide a centralized pool of organizational knowledge, readily available to all team members.
- AI Knowledge Base Software: These tools enhance knowledge accessibility:
- Intuitive Searching: With natural language processing, users can search using colloquial terms, bypassing technical jargon.
- Automated Content Creation: AI sources answers directly from existing company documents, making information access faster.
- Content Curation: AI flags and revises outdated information, ensuring up-to-date knowledge repositories.
- Efficient Organization: AI auto-tags and categorizes data, making the knowledge base user-friendly.
Encouraging Knowledge Exchange & Sharing
In an evolving corporate world, fostering a culture of knowledge sharing is essential for adaptability and innovation. A staggering 75% of organizations see knowledge sharing as crucial for success in the coming years.
However, simply recognizing the importance isn’t enough. Organizations need actionable knowledge sharing techniques:
- Structured Programs: Initiatives like “Tech Tuesday” or “Feature Friday” sessions can be instrumental. Companies can ensure regular knowledge dissemination by dedicating specific days for sharing updates, discoveries, or insights.
- Leveraging Platforms: Given the costs associated with onboarding, structured platforms save resources and ensure an effective knowledge transition.
- Creating Knowledge Ambassadors: Designate and train certain team members to champion and inspire knowledge exchange.
- Understanding Knowledge Management Systems: Incorporating platforms that facilitate easy knowledge exchange and gap identification is crucial. These systems to capture knowledge can be used to bridge the gaps and set the stage for ongoing innovation.
The Power of a Knowledge Management Solution
In our information-rich era, knowledge management solutions are more than tools—they’re essential strategies. These systems preserve and share vital knowledge assets, enabling organizations to leverage collective expertise:
The benefits of implementing a knowledge management solution include:
- Knowledge Retention: Addressing the challenge of expertise loss, these systems capture, store, and make available crucial insights.
- Centralizing Critical Knowledge: This breaks down knowledge silos, ensuring accessible and timely insights for all.
- Streamlining Knowledge Flow: An efficient system ensures that everyone, from management to new staff, has access to collective wisdom, aiding informed decisions and teamwork.
- Driving Innovation and Growth: As information overload becomes commonplace, filtering and accessing relevant data becomes critical. Knowledge management software solutions support this, optimizing processes and sparking innovation.
Harnessing the power of a knowledge management solution is crucial for modern businesses. By enhancing knowledge retention, promoting efficient sharing, and facilitating the flow of knowledge, these solutions lay the groundwork for informed decision-making, collaboration, and sustainable growth.
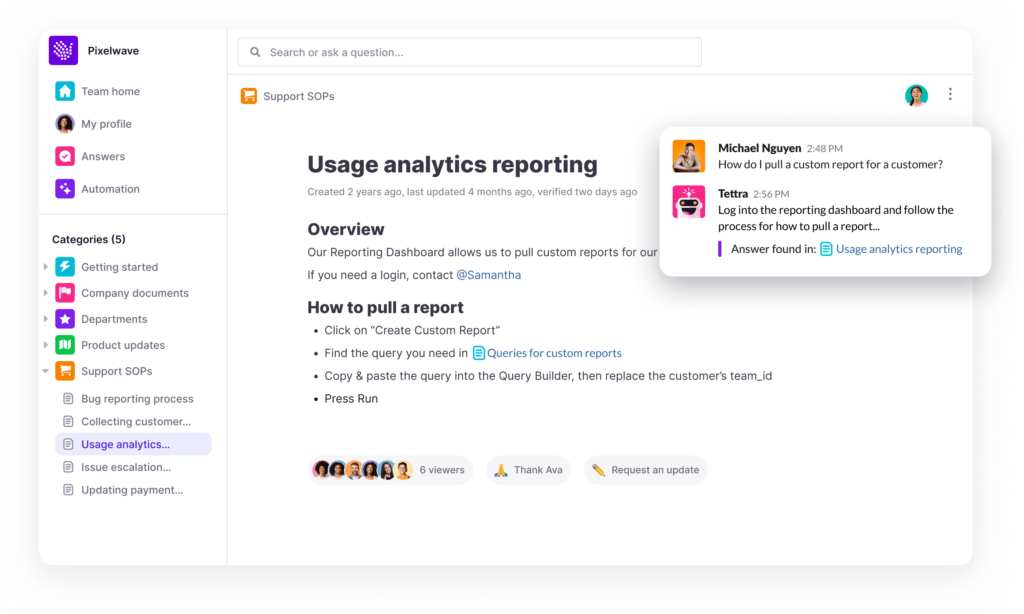
Try Tettra for sharing and managing your knowledge gaps at work.
With Tettra, you’ll get:
- Q&A workflow to capture questions
- AI-powered knowledge base software to document answers
- Knowledge management features to keep content up to date.
- Integrations with Slack, MS Teams, Google Docs, Github and Zapier to help your team answer and capture knowledge quickly
Learn how Tettra can help you share knowledge more efficiently and effectively at your company.





