What is knowledge transfer?
Knowledge transfer refers to the process through which one unit (e.g., individual, group, department, organization) is affected by the experience of another. It is the dissemination of knowledge from one part of an organization to another or from one individual to another.
This process ensures that valuable information, skills, and expertise are not lost but shared and utilized across the organization. A well-designed knowledge transfer plan is essential to facilitate this flow of information effectively.
The Channels of Knowledge Transfer
Formal Channels
- Training Programs: Structured learning sessions designed to impart specific skills and knowledge.
- Documentation: Manuals, guides, and standard operating procedures (SOPs) that capture essential information.
- Workshops and Seminars: Interactive sessions that encourage knowledge exchange and skill development.
- Knowledge Management Systems (KMS): Digital platforms that store, organize, and facilitate access to organizational knowledge.
Informal Channels
- Mentoring and Coaching: One-on-one guidance and support provided by more experienced employees.
- Peer-to-Peer Networks: Collaborative relationships among employees that foster the sharing of insights and expertise.
- Social Interactions: Casual conversations and social gatherings where knowledge is exchanged informally.
- Communities of Practice (CoPs): Groups of people who share a concern, a set of problems, or a passion about a topic and deepen their knowledge by interacting on an ongoing basis.
The ability to transfer knowledge effectively is crucial for maintaining a competitive edge.
Organizations that have their knowledge transfer process down pat can innovate faster, adapt to changes more readily, and improve their overall performance.
A knowledge transfer strategy is key to navigating this landscape successfully.
⭐️ More about knowledge management from Tettra:
Challenges in Implementing Knowledge Transfer
- Cultural Barriers: Differences in organizational culture can hinder the sharing of knowledge.
- Lack of Trust: Employees may be reluctant to share knowledge if there is a lack of trust within the organization.
- Geographical Dispersion: Distributed teams can face difficulties in effective knowledge sharing due to physical distance.
- Technological Barriers: Inadequate or incompatible technology can impede the transfer of knowledge.
- Resistance to Change: Employees may resist new ways of working and sharing knowledge.
Best Practices in Knowledge Transfer
- Foster a Knowledge-Sharing Culture: Encourage and reward knowledge-sharing behaviors.
- Implement Robust KMS: Invest in technologies that support knowledge capture, storage, and retrieval.
- Facilitate Continuous Learning: Provide ongoing training and development opportunities.
- Leverage Multiple Channels: Use a combination of formal and informal channels for knowledge transfer.
- Measure and Improve: Regularly evaluate the effectiveness of knowledge transfer initiatives and make necessary adjustments.
Process of Knowledge Transfer
Step 1: Identification and Documentation of Knowledge
Identify critical knowledge, including tacit knowledge (intangible, experience-based) and explicit knowledge (tangible, documented), and document it systematically to ensure it is accessible and understandable.
Step 2: Documentation and Organization of Knowledge
Organize the documented knowledge in a structured manner using knowledge management systems and tools. A comprehensive knowledge management platform can be invaluable in this step.
Step 3: Transfer of Knowledge
Implement mechanisms for sharing knowledge, such as training sessions, mentoring, and knowledge repositories. This step ensures that knowledge gaps are identified and addressed.
Step 4: Evaluation and Feedback
Assess the effectiveness of knowledge transfer efforts and gather feedback from participants. This helps in refining the knowledge transfer process.
Step 5: Continuous Improvement
Continuously refine knowledge transfer processes based on feedback and changing organizational needs. Regular updates and iterations ensure the process remains relevant and effective.
Step 6: Measurement and Reporting
Track and report on key metrics to measure the impact of knowledge transfer initiatives on organizational performance. This data-driven approach helps in optimizing the knowledge transfer strategy.
Benefits of Knowledge Management
Standardization: Documented processes ensure consistency and efficiency, reducing errors and increasing work speed.
Resource Utilization: Allocates resources effectively, using data and metrics to guide decisions and optimize productivity.
Enhanced Employee Empowerment and Engagement: Quick access to information boosts autonomy and job satisfaction by enabling informed decision-making.
Reduced Operational Redundancies: Proven methods and documented solutions eliminate repetitive tasks and streamline operations.
Retained Organizational Knowledge: Captures and preserves valuable insights, ensuring continuity and long-term success.
Innovation: Access to diverse insights fosters creativity and the development of groundbreaking solutions.
Learning Culture: Encourages continuous learning and knowledge transfer, enhancing overall organizational performance.
⭐️ Go deeper on the benefits of knowledge management.
Barriers to Effective Knowledge Transfer
- Lack of Incentives: Employees may not be motivated to share knowledge without proper incentives.
- Inadequate Infrastructure: Poor technological support can hinder knowledge sharing efforts.
- Information Overload: Excessive information can overwhelm employees and reduce the effectiveness of knowledge sharing.
- Silos: Organizational silos can prevent the flow of information between departments.
Guiding Principles of Effective Knowledge Sharing
- Transparency: Encourage openness and accessibility of information.
- Collaboration: Promote teamwork and collaborative efforts.
- Relevance: Ensure the knowledge shared is relevant and useful to the recipient.
- Timeliness: Share knowledge in a timely manner to maximize its impact.
- Respect: Value and respect the knowledge and contributions of others.
⭐️ Learn more about knowledge sharing at work
Examples of Knowledge Transfer in Different Industries
Example 1: Knowledge Transfer in Healthcare – The Mayo Clinic
The Mayo Clinic is renowned for its effective knowledge transfer practices, which significantly improve patient care.
One of their key strategies is the use of an extensive electronic health record (EHR) system.
This system ensures that patient information is accessible to healthcare professionals across different departments and locations.
The Mayo Clinic also emphasizes collaborative case discussions, where multidisciplinary teams review complex cases and share insights, leading to more accurate diagnoses and effective treatments.
Example 2: Knowledge Transfer in Manufacturing – Toyota
Toyota’s success is largely attributed to its effective knowledge transfer practices, particularly through the Toyota Production System (TPS). One of the key components of TPS is the “kaizen” philosophy, which emphasizes continuous improvement and knowledge sharing among employees. Toyota encourages workers at all levels to contribute ideas for improving processes, and these ideas are documented, shared, and implemented across the organization.
Example 3: Knowledge Transfer in Aerospace – NASA
NASA has a robust knowledge management program to ensure that critical information and expertise are shared across its missions.
One notable initiative is the NASA Engineering Network (NEN), a centralized repository where engineers can access technical reports, lessons learned, and best practices from past projects. This system enables NASA to apply knowledge from previous missions to new challenges, reducing risks and enhancing mission success.
Get more tips about knowledge management from Tettra:
- What is knowledge management software? (20 things to know)
- 8 examples of knowledge management systems
- Here’s your knowledge management strategy
- 11 best knowledge management tools to use right now
How to Use Tettra to Improve Knowledge Transfer at Your Company
Tettra is a powerful knowledge management tool designed to enhance knowledge transfer within organizations.
By leveraging Tettra, companies can ensure that critical information is easily accessible, well-organized, and effectively shared among team members.
Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to use Tettra to improve knowledge transfer at your company:
1. Set Up Your Tettra Workspace
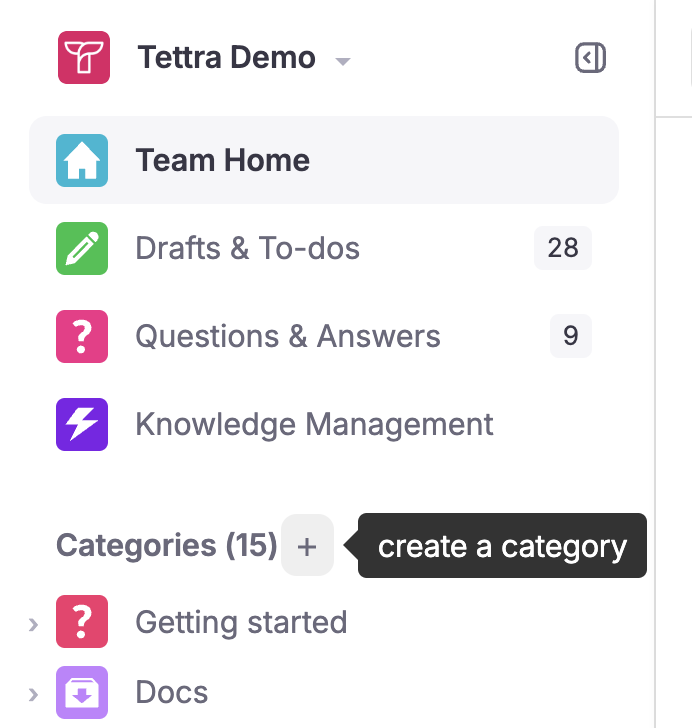
- Create a Structure: Organize your Tettra workspace by creating categories and subcategories that reflect your company’s departments, projects, and functions. This will make it easier for team members to find and contribute knowledge.
- Standardize Templates: Use Tettra’s template feature to create standardized formats for common documents, such as meeting notes, project plans, and how-to guides. This ensures consistency and completeness in documentation.
2. Document and Centralize Knowledge
- Start with Key Information: Identify critical knowledge areas that need documentation. This could include standard operating procedures (SOPs), project workflows, company policies, and frequently asked questions (FAQs).
- Use Integrations: Integrate Tettra with other tools your company uses, such as Slack, Google Drive, and GitHub. This allows seamless import and linking of existing documents, ensuring that all relevant knowledge is centralized in Tettra.
- Encourage Contributions: Encourage team members to document their processes, insights, and best practices. Recognize and reward contributions to foster a culture of knowledge sharing.
3. Implement Best Practices for Knowledge Transfer
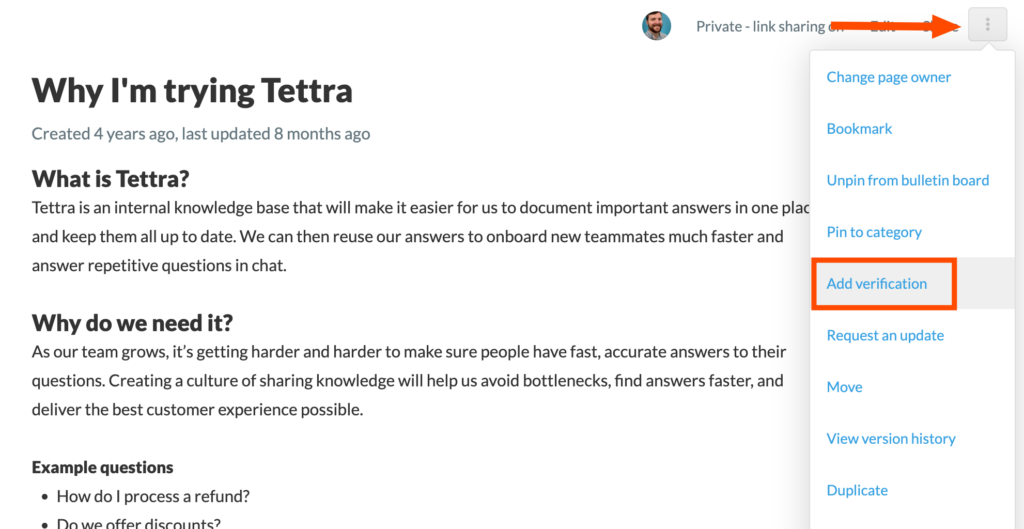
- Regular Updates, Reviews and Verification: Schedule regular reviews of documents to ensure they remain relevant and accurate. Assign ownership to specific team members for maintaining, updating and verifying for accuracy.
- Training and Onboarding: Incorporate Tettra into your training and onboarding programs. New hires can quickly get up to speed by accessing a centralized repository of essential knowledge.
- Measure and Improve: Use Tettra’s analytics to track engagement and usage. Analyze which documents are most accessed and which areas may need more attention. Continuously improve your knowledge management practices based on these insights.
4. Leverage Tettra for Specific Knowledge Transfer Needs
- Onboarding & Hiring: List your key processes and SOPs to new hires to help them start right away
- Project Documentation: Document project plans, timelines, and milestones in Tettra. Use it to track progress and share updates with the team.
- Customer Support: Create a comprehensive knowledge base for customer support. Document common issues, solutions, and troubleshooting guides to help support staff resolve customer queries efficiently.
- Sales and Marketing: Store product information, sales pitches, marketing strategies, and competitive analysis in Tettra. Ensure that sales and marketing teams have access to the latest information to drive success.





