Business owners and leaders often need more information, expertise, or knowledge to make the right decisions.
Good business owners know who in their company has the knowledge to help the organization move forward and aren’t afraid to ask for their help.
However, the challenge with this approach is that key decision-makers can’t always pinpoint who in their company has the knowledge to deal with specific challenges. Or can they?
With knowledge mapping, business organizations can create large visual databases of collective knowledge that can easily be accessed and utilized based on current needs. Today, we’ll talk about knowledge mapping and how it can be used effectively.
What is Knowledge Mapping?
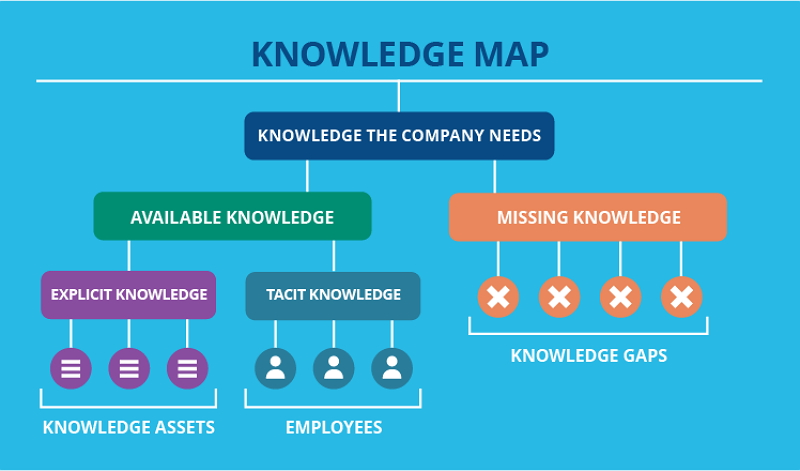
Knowledge mapping is a knowledge management method for creating visual representations of knowledge assets within a business.
Knowledge mapping involves maps or diagrams containing essential knowledge elements, relationships, and key bottlenecks contributing to the overall knowledge resource.
It’s a very simple visual aid that connects all related information to give the right directions. A knowledge map can include resources like documentation, files, or individual information on your employees’ skills or knowledge. There are many different types of knowledge mapping techniques.
However, at their core, they all focus on three important things: knowing what, how, and why. By visualizing all knowledge resources, companies can recognize potential gaps and organize a better flow of information. They make it easy to find relevant information.
Benefits of Knowledge Mapping
There are many benefits of knowledge mapping. However, here are the key advantages:
Improved Knowledge Sharing
As mentioned, knowledge maps visually represent complex and relevant information. Every individual can access and understand this information, and with this visualization, users can understand relationships and ideas more accurately.
Knowledge maps are centralized repositories, and anyone can access them. All the information is placed in a single platform, and users can understand greater context and how small pieces fit together. Everyone can access the same platform and share specific parts with their coworkers to get on the same page.
Identification of Knowledge Gaps
Not only does knowledge mapping help find the correct information needed to continue further, but it also helps employees recognize missing information and identify knowledge gaps.
Knowledge maps can also show the relationships between two knowledge resources.
Anyone can access knowledge maps, and users can leave feedback and insights into potentially overlooked areas or trends that have yet to be addressed.
Enhanced Organizational Learning
Knowledge maps improve organizational learning in different ways. First, since complex information is broken down into smaller and more understandable parts, it is easier for people to learn from it. Second, employees learn passively by using the knowledge map.
They constantly share information and have easy access to any knowledge they might need. Knowledge maps can also help with onboarding and training by giving new employees a centralized repository with clear information on organizational processes and knowledge.
Types of Knowledge Maps
Not all knowledge maps are created equal (some smart guy, probably). But yes, there are different types of knowledge maps depending on how they represent knowledge and the main focus.
Concept Maps
Concepts or conceptual maps provide more information on specific topics or ideas. Their main idea branches out to different ideas, concerns, or issues. These maps let you see how different issues are related to the original topic.
In most cases, new subtopics have additional links to other resources. This method is good for businesses with complex processes like supply chains, as it allows them to fix each subtopic while ensuring that the whole topic isn’t disrupted.
Mind Maps
Mind maps are great for brainstorming ideas organically while having less rigid structure and freedom. Mind maps are diagrams that represent items, concepts, words, or tasks that are linked and placed around the main subject.
For example, you can start with a single concept at the center and connect it with related ideas to create a visual web. It’s an excellent option for organizations that brainstorm ideas, solve problems, or make timely decisions.
Process Maps
Process maps or process mapping is a knowledge mapping method that allows organizations to understand their processes and recognize areas for improvement. They are usually used to create visual representations of business workflows so that organizations can understand key components.
These tools allow organizations to streamline their workflows by understanding all required steps, the issues with those steps, and potential solutions that can be introduced. Organizations have a broader overview of processes and can dig into tinier details of their steps.
APQC’s Process-based Knowledge Map
The American Productivity & Quality Center knowledge map is a tool that allows organizations to symmetrically leverage, organize, and capture knowledge while understanding the context of business processes. The amp aligns all business processes and knowledge related to them.
APQC’s knowledge map visually represents relationships between processes and knowledge assets. That makes locating knowledge easier and helps us understand where it can be applied.
APQC offers various tools that provide the best benchmarking data organizations can use to compare management practices.
Knowledge Mapping Process
Step 1: Identify the Knowledge to Map
Start by defining the objectives of knowledge mapping. Focus on essential business processes and understand where knowledge is needed and how it moves through the organization.
Talk to your employees and key stakeholders to identify the most important knowledge and how it’s currently being used. Align the map with your key strategic priorities to get the most out of it.
Step 2: Select the Appropriate Mapping Technique
When selecting the proper mapping technique, consider your organization’s resources, goals, processes, and context. The platform and method you choose should be easy to use, meet all your data management requirements, and align with your overall organization and culture.
Step 3: Gather Relevant Knowledge Assets
The next step is to use the key guidelines you’ve set for the knowledge you want to map to identify and gather relevant knowledge assets.
Gather as much knowledge as possible while making sure it’s relevant to the goals you want to achieve.
Step 4: Analyze and Synthesize the Knowledge
Before you start analyzing knowledge synthesis, be clear about your focus. Locate all sources and ensure they are current, reliable, and relevant to ensure you add only quality knowledge.
After evaluating your sources, analyze and compare them to identify gaps, main themes, or irregularities. Organize and structure your synthesis with connections, transitions, headings, and subheadings.
Step 5: Create the Knowledge Map
The next step is to pick a knowledge map tool or platform and create your knowledge map. Consider using a template for your knowledge map method and follow the steps adequately.
Map out relationships between different knowledge. Remember that your initial map won’t be perfect, but that’s perfectly fine.
Step 6: Review and Update the Knowledge Map
Once your knowledge map is completed, make a conscious effort to review and improve it. Always look for opportunities to improve the knowledge flow, analyze usability, improve accessibility, and ensure that the knowledge within the map is relevant and current.
Key Elements of Knowledge Mapping
Tacit Knowledge vs. Explicit Knowledge
The two most essential types of knowledge regarding knowledge mapping for business purposes are tacit and explicit.
Tacit knowledge is information learned through experience, which is the type of knowledge you can’t accurately describe in your knowledge map.
Instead, you should make entries that allow individuals to perform one-on-one mentoring and training to transfer this information to your employees. On the other hand, explicit knowledge can be easily documented and shared with others.
Training manuals or video tutorials are typical examples of tacit knowledge, and ideally, your knowledge map should have a lot of it.
Intellectual Capital and Critical Knowledge
Intellectual capital is all your employees’ experiences, skills, and knowledge. In other words, it’s the knowledge your employees possess. Critical knowledge is the skills and information that are essential for completing specific processes and achieving business goals.
Integrating both of these in your knowledge map is essential because it allows you to recognize people with the skills for specific tasks and locate the knowledge required for finishing those tasks.
Flow of Knowledge within Organizations
It’s important to ensure knowledge flow throughout the organization when creating a knowledge map. Start with a centralized concept around an essential topic. Add subtopics and branches related to the main topic and further break them down into subtopics that offer more detailed ideas.
Take the time to create relevant connections and links to showcase relationships between different branches. Rely on various visual elements to make the map more engaging and improve understanding.
Role of Employees as Creators of Knowledge
Employees play an important role in creating and maintaining knowledge maps. Their involvement can be the difference between accurate and inaccurate knowledge maps.
That’s why it’s crucial to introduce things like knowledge validation, subject matter experts, process owners, and knowledge managers.
They can verify and improve knowledge while having the proper authority to make the necessary changes. Consider setting information curators to categorize, structure, update, and maintain knowledge.
Knowledge Mapping Tools and Software
You can utilize various knowledge mapping tools to create a knowledge map for your organization. Here are some of the key considerations when choosing one.
Mind Mapping Platforms
The first thing is to consider the tasks that you want to do with your mapping tool. That helps you find the right functionalities within a mind-mapping platform. On the other hand, if you want to use knowledge maps to improve planning, looking for platforms offering extensive task management features is probably a good idea.
Look for a platform that allows you to use the proper knowledge mapping method and has all the functionalities to execute flawlessly. Ultimately, ease of use is a constant factor any organization needs to ensure everyone can quickly learn how to use the platform.
Cloud-based Tools for Real-time Collaboration
If you’re looking for a knowledge map that offers real-time collaboration the most cost-effective option is to go with a cloud-based tool.
These tools offer easy access and allow users to share maps with anyone else while working on changes together. When looking for a cloud-based solution with real-time collaboration, consider features like history of changes, commenting, voting, shareability, etc.
Internal Knowledge Base Software
“An internal knowledge base (or internal KB) is the single source of truth.”
Knowledge bases are centralized repositories that store all of your company’s knowledge. Everyone within the organization has access and can locate, share, and retrieve any information.
A good internal knowledge base lets users search for information, collaborate, share information, and learn from the knowledge base.
It’s a simple but effective way of storing your knowledge maps because you can easily create a hierarchy of who can make changes, see updates in real-time, and get efficient storage available only to your organization.
Mapping your knowledge might seem like a lot of work, but it’s become much easier with modern knowledge-base solutions and cloud-based platforms. As Thomas Jefferson said, knowledge is power! It can help you improve your overall business operations and bottom line while streamlining processes and boosting efficiency.
Get more tips about knowledge management from Tettra
- What is knowledge management? The basics explained
- What is knowledge management software? (20 things to know)
- 5 steps of the knowledge management process
- Process mapping: Your guide & tips
- 11 best knowledge management tools to use right now
Why use Tettra as your internal knowledge base
Tettra is an AI-powered knowledge management system that helps you curate important company information into a knowledge base, use it to answer repetitive questions in Slack and keep it up-to-date, organized, and complete with automation.
With Tettra, you’ll have a full suite of tools for sharing knowledge.
- Q&A workflow to capture questions
- AI-powered knowledge base software to document answers
- Knowledge management features to keep content up to date.
- Integrations with Slack, Google Docs, Github and Zapier to help your team answer and capture knowledge quickly